반응형
SORTING
df = pd.DataFrame({'Employee ID':[111, 222, 333, 444],
'Employee Name':['Chanel', 'Steve', 'Mitch', 'Bird'],
'Salary [$/h]':[35, 29, 38, 20],
'Years of Experience':[3, 4 ,9, 1]})
df
# 경력을 오름차순으로 정렬
df.sort_values('Years of Experience')
# 내림차순으로 정렬
df.sort_values('Years of Experience', ascending= False)
# 이름과 경력으로 정렬하되,
# 이름은 내림차순, 경력은 오름차순으로 정렬
df.sort_values( ['Employee Name','Years of Experience'], ascending=[False,True] )
CONCATENATING AND MERGING
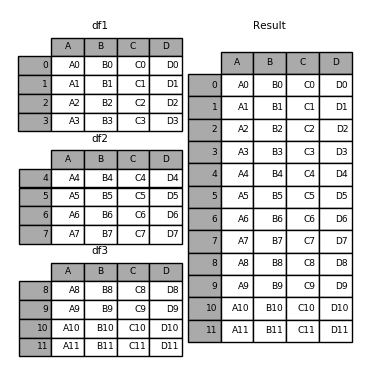
Reference: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/merging.html
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']},
index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7'],
'D': ['D4', 'D5', 'D6', 'D7']},
index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
df3 = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A8', 'A9', 'A10', 'A11'],
'B': ['B8', 'B9', 'B10', 'B11'],
'C': ['C8', 'C9', 'C10', 'C11'],
'D': ['D8', 'D9', 'D10', 'D11']},
index=[8, 9, 10, 11])
.concat([,])

# Creating a dataframe from a dictionary
raw_data = {
'Employee ID': ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'],
'first name': ['Diana', 'Cynthia', 'Shep', 'Ryan', 'Allen'],
'last name': ['Bouchard', 'Ali', 'Rob', 'Mitch', 'Steve']}
df_Engineering_dept = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['Employee ID', 'first name', 'last name'])
df_Engineering_dept
raw_data = {
'Employee ID': ['6', '7', '8', '9', '10'],
'first name': ['Bill', 'Dina', 'Sarah', 'Heather', 'Holly'],
'last name': ['Christian', 'Mo', 'Steve', 'Bob', 'Michelle']}
df_Finance_dept = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['Employee ID', 'first name', 'last name'])
df_Finance_dept
df_all = pd.concat([df_Engineering_dept,df_Finance_dept],)
raw_data = {
'Employee ID': ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '7', '8', '9', '10'],
'Salary [$/hour]': [25, 35, 45, 48, 49, 32, 33, 34, 23]}
df_salary = pd.DataFrame(raw_data, columns = ['Employee ID','Salary [$/hour]'])
df_salary
# 데이터프레임 딱 두개를 연결고리가 되는 컬럼으로 함치려고 할때
.merge()# merge는 데이터프레임 두개만 가지고 하는 것
# 첫번째 데이터프레임을 left라고 하고,
# 두번째 데이터프레임을 right라고 한다.
pd.merge( df_all, df_salary, on='Employee ID')
# how=는 left를 기준으로 없는데이터까지 포함해서 data frame을 출력 할 때 사용
pd.merge( df_all, df_salary, on='Employee ID', how='left')
반응형
'Library > PANDAS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PYTHON PANDAS - Pivot Table (0) | 2022.05.05 |
|---|---|
| PYTHON PANDAS - DATA FRAME PLOT (CHART) (0) | 2022.05.03 |
| PYTHON PANDAS - PANDAS OPERATIONS & APPLYING FUNCTION (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| PYTHON PANDAS - Loading Data & Categorical Data (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| PYTHON PANDAS - NaN (0) | 2022.04.28 |



